In the world of finance and accounting, data is the bedrock of every decision, from routine bookkeeping to high-level strategic forecasting. Migrating this critical asset—whether to a new accounting system, a cloud platform, or during a merger—is a high-stakes operation. A single misstep can lead to corrupted financial records, serious compliance breaches, and costly operational downtime. To ensure a seamless and secure transition, a well-defined strategy isn't just helpful; it's absolutely essential.
This guide outlines the eight most critical best practices for data migration, providing a comprehensive roadmap to de-risk your project. We’ll help you guarantee that your sensitive financial data arrives at its new destination intact, accurate, and ready for immediate business use. The following points move beyond generic advice to give you actionable steps, real-world examples, and the strategic foresight needed for a successful migration.
The process often involves complex technical components, such as moving the underlying databases that power your financial applications. To delve deeper into specific strategies for these core systems, which often form a critical part of overall data migration efforts, consult resources on effective database migration best practices.
By following these structured guidelines, you can transform a potentially chaotic project into a controlled, predictable, and successful initiative. Let’s explore the key practices that will protect your data integrity and support your organization’s growth.
1. Comprehensive Data Assessment and Profiling
Before a single byte of financial data is moved, a successful migration begins with a deep, forensic understanding of its source. This foundational step, known as data assessment and profiling, is one of the most critical best practices for data migration. It involves a meticulous analysis of the quality, structure, completeness, and consistency of your existing datasets, from historical general ledgers to client investment portfolios. It’s about creating a detailed inventory of all data assets and reverse-engineering the business rules that govern them.

This proactive discovery phase is crucial for identifying potential roadblocks long before they can derail the migration. A thorough profile provides the essential blueprint for accurate planning, intelligent transformation logic, and realistic timelines. For instance, discovering that 15% of your legacy client records have inconsistent address formatting allows you to build a cleansing rule before the migration, not after it causes errors in your new CRM.
Why It's a Foundational Step
Think of it as the due diligence phase for your data. Skipping this step is like building a new headquarters without surveying the land first; you risk building on an unstable foundation. In a financial context, the stakes are exceptionally high. An unprofiled dataset could hide orphaned transaction records, null values in critical compliance fields, or duplicate customer entries that, if migrated as-is, could lead to severe reporting errors and regulatory penalties.
A prime example is JPMorgan Chase's rigorous data profiling initiative before migrating customer data into new CRM systems. By analyzing millions of records first, they identified and resolved data quality issues that would have otherwise compromised customer service and sales analytics in the new environment.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively execute this practice, consider the following strategies:
- Utilize Automated Tools: Leverage automated profiling tools like Talend Data Quality or Informatica Data Quality. These platforms can scan entire databases and rapidly identify patterns, data types, value frequencies, and anomalies that are impossible to spot manually.
- Involve Business Users: Engage accountants, financial analysts, and compliance officers early. They possess invaluable context about the data, understanding the business logic behind why certain fields are populated a specific way.
- Create Data Quality Scorecards: Quantify your findings. Develop scorecards that rate critical data elements (e.g., Customer TIN, transaction dates) on metrics like completeness, validity, and uniqueness. This provides a clear baseline to measure post-migration improvement.
- Document in a Central Catalog: Don't let your findings get lost in spreadsheets. Document all data profiles, business rules, and quality issues in a centralized data catalog. This becomes an invaluable resource for the entire project team.
2. Detailed Migration Planning and Strategy Development
Once you have a comprehensive map of your data, the next step is to architect the journey. A detailed migration plan and strategy serve as the master blueprint for the entire project, moving beyond what data you have to how, when, and by whom it will be moved. This is one of the most essential best practices for data migration, as it translates the initial assessment into an executable roadmap, complete with timelines, resource allocations, risk mitigation, and clear success criteria.
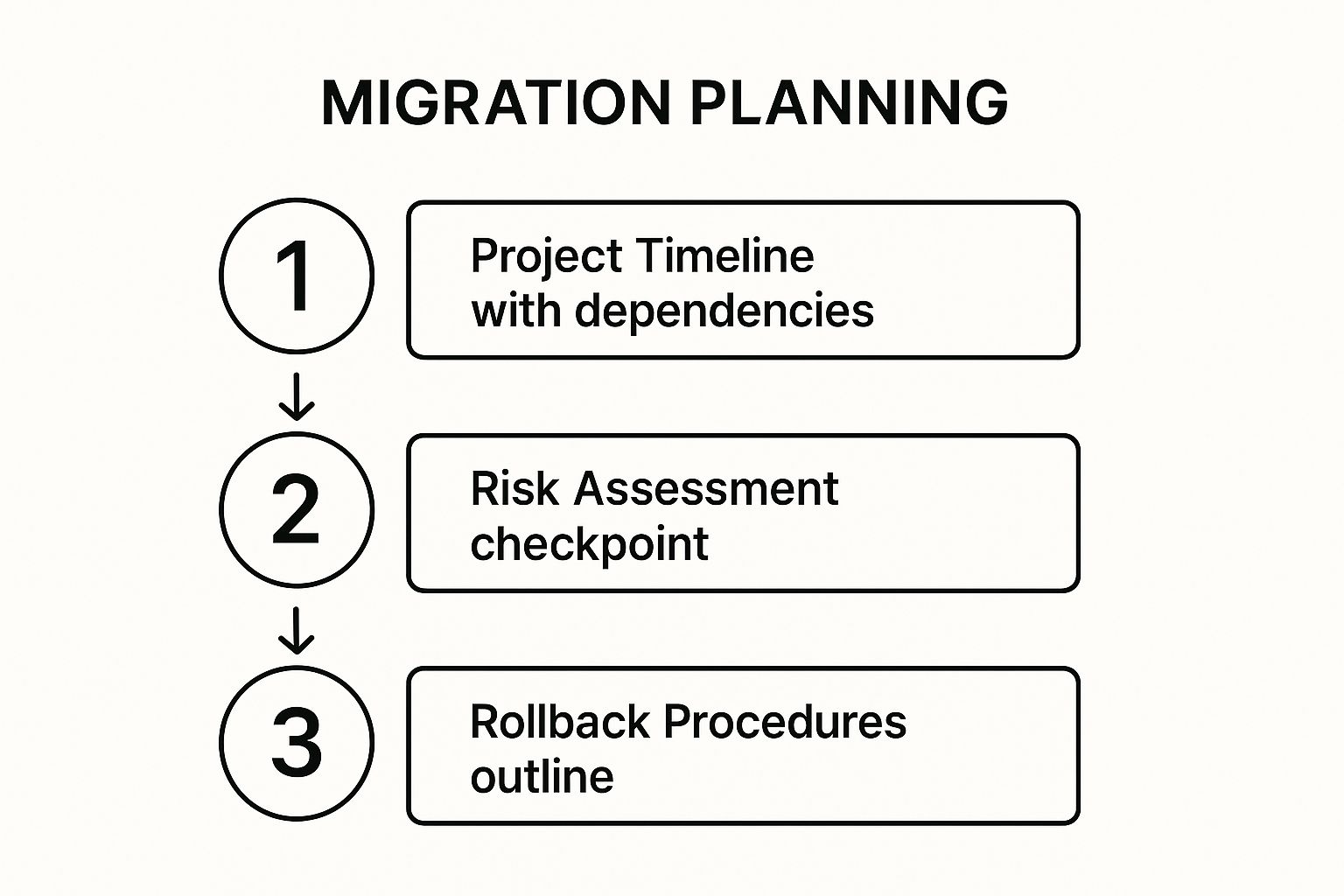
A well-defined strategy prevents the project from devolving into a chaotic, reactive exercise. It forces stakeholders to decide on a migration pattern, such as a phased (or trickle) migration versus a "big bang" approach where all data is moved at once. The infographic above illustrates a simplified core planning process, showing how a timeline must inform risk assessment, which in turn necessitates having a defined rollback procedure. This sequential thinking ensures that for every planned action, there is a corresponding contingency plan.
Why It's a Foundational Step
Without a robust strategy, a data migration is merely a high-stakes gamble. This plan is your governance framework, defining the rules of engagement and ensuring every action is deliberate and aligned with business objectives. In the financial sector, where downtime can translate to millions in lost revenue and regulatory fines, this strategic foresight is non-negotiable. It dictates how you will maintain operational continuity and data integrity throughout the transition.
Consider Capital One’s multi-year cloud transformation. Instead of a single, monolithic move, they adopted a phased migration strategy, moving applications and their associated data incrementally. This meticulous planning allowed them to manage risk, learn from each phase, and avoid disrupting critical customer-facing banking services. The strategy was the bedrock of their successful transition from legacy data centers to the cloud.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To develop a robust migration plan and strategy, focus on these concrete actions:
- Define Clear Success Metrics: Establish specific, measurable acceptance criteria before you start. This could include metrics like "99.9% of customer records reconciled" or "post-migration financial report generation time reduced by 30%." These criteria are vital for your financial reporting best practices.
- Build in Buffer Time: No migration goes perfectly. Allocate a contingency buffer, typically 20-30% of the projected timeline, to accommodate unforeseen technical challenges, data quality issues, or resource constraints.
- Create Detailed Rollback Procedures: Hope for the best but plan for the worst. Document a step-by-step rollback plan that can be executed quickly if the migration fails to meet its critical success criteria. This plan should be tested and validated beforehand.
- Schedule During Low-Usage Periods: Minimize business disruption by planning the final cutover during off-peak hours, such as a weekend or holiday, when system usage is at its lowest. Communicate this schedule clearly to all stakeholders.
3. Robust Data Backup and Recovery Procedures
A data migration, especially in a financial context, is an inherently risky procedure. The process of extracting, transforming, and loading critical data introduces multiple points of potential failure. That's why implementing robust data backup and recovery procedures is one of the most non-negotiable best practices for data migration. This involves more than just running a pre-migration backup; it’s about creating a comprehensive safety net that protects your data at every stage and guarantees you can revert to a stable state if something goes wrong.
This practice ensures business continuity by creating secure, validated copies of your source data before any changes are made. It also includes having a documented and tested rollback plan. If a critical error is discovered midway through loading data into your new accounting platform, you need the ability to quickly and cleanly restore the original system to its pre-migration state, minimizing downtime and data corruption.
Why It's a Foundational Step
Think of this as your project's insurance policy. Migrating data without a tested recovery plan is like performing high-wire acrobatics without a net. The potential for catastrophic data loss, whether due to script errors, hardware failure, or human mistake, is too significant to ignore. In finance and accounting, losing transaction histories or client financial records, even temporarily, can lead to severe operational chaos, loss of customer trust, and major compliance violations.
A prime example is Spotify's meticulous approach when migrating user playlist data. They used incremental backups and staged rollouts, ensuring that if any single batch failed, they could instantly roll it back without affecting the entire user base. This minimized risk and ensured a seamless user experience throughout a massive infrastructure change. A fundamental component of any migration plan is to understand how to backup organization data effectively before initiating any such complex project.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively execute this practice, consider the following strategies:
- Follow the 3-2-1 Backup Rule: Maintain at least three copies of your data, store them on two different types of media, and keep one of those copies in an offsite location. This classic rule, popularized by backup solutions like Veeam and AWS Backup, protects against a wide range of failure scenarios.
- Test Your Restore Procedures: A backup is useless if it can't be restored. Regularly conduct trial restorations to a sandboxed environment to verify the integrity of your backups and confirm your team can execute the recovery process efficiently under pressure.
- Document the Rollback Plan: Create a step-by-step guide detailing the exact procedures for rolling back the migration at each phase. This document should be clear, concise, and accessible to the entire migration team.
- Retain Backups Post-Migration: Do not discard your pre-migration backups immediately after the go-live. Keep them until the new system has been fully validated over a significant period (e.g., after a full financial quarter-end close) to ensure no subtle data corruption has occurred.
4. Incremental and Phased Migration Approach
Attempting to migrate an entire financial ecosystem in a single, "big bang" event is a high-stakes gamble. A far more strategic and risk-averse method is an incremental and phased migration. This is one of the most critical best practices for data migration, as it involves breaking the monolithic project into smaller, distinct, and manageable phases. Each phase can be executed, tested, and validated independently, dramatically reducing the scope of potential failures at any given time.
This approach creates faster feedback loops, allowing the project team to learn and apply lessons from early phases to subsequent ones. Instead of a single point of failure, you create a series of controlled, low-impact deployments. For instance, you might migrate historical, non-critical ledger data first, followed by vendor payment histories, and finally, live transactional data, refining your process at each step.
Why It's a Foundational Step
A phased approach transforms a daunting, high-risk marathon into a series of achievable sprints. This significantly minimizes business disruption, as only a small subset of data or functionality is in transition at any moment. For financial institutions, this means core operations like payroll processing or client trading can continue uninterrupted while less critical data modules are migrated and validated in the background.
A well-known example is Salesforce's strategy for migrating customer instances during major platform upgrades. They don't move all customers at once. Instead, they migrate them in carefully planned waves, allowing them to manage technical support resources effectively, identify issues within a small cohort, and ensure a stable transition for their entire user base. This incremental process is key to their platform's reliability.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively execute a phased migration, consider the following strategies:
- Prioritize with Business Impact: Begin with data that is less critical or has fewer dependencies. This allows your team to build confidence and refine the migration scripts and validation processes in a low-risk environment before tackling high-stakes data like customer accounts or active portfolios.
- Ensure Each Phase Delivers Value: Structure each phase to deliver a tangible business benefit, such as decommissioning a legacy server or enabling a new reporting feature. This helps maintain project momentum and demonstrates continuous progress to stakeholders.
- Plan for Data Synchronization: During the transition, you will have two systems of record. Implement a robust data synchronization or dual-write strategy to ensure data consistency between the legacy and new systems until the old one is fully decommissioned.
- Use Feature Flags for Control: Employ feature flags or other routing mechanisms to direct traffic and data processing. This allows you to gradually shift users or workflows to the new system and provides an immediate rollback capability if an issue is discovered in a specific phase.
5. Comprehensive Data Validation and Quality Testing
Data migration isn't complete once the data lands in the new system; it's complete once that data is proven to be accurate, complete, and trustworthy. This is where rigorous validation and quality testing come into play, serving as one of the most essential best practices for data migration. This stage involves a multi-layered approach to verifying data integrity at every step, from initial extraction to post-load reconciliation, ensuring the migrated data is fit for its intended business purpose.
This systematic verification process is non-negotiable in financial contexts. It moves beyond simple row counts to include complex business rule validation, checksums, and reconciliation reports. The goal is to build an auditable trail that proves the data has not been corrupted or lost and that all transformations have been applied correctly, confirming the new system can be relied upon for critical financial reporting and operations.
Why It's a Critical Checkpoint
Think of this step as the final quality control inspection on a manufacturing line. Without it, you are effectively shipping a potentially defective product to your end-users. In a financial migration, a single misplaced decimal in a transaction table or a mis-mapped customer ID can cascade into catastrophic errors, from incorrect financial statements to failed regulatory audits. Proper validation is the critical safeguard that prevents these issues from ever reaching production.
A powerful example is Bank of America's meticulous validation framework for its regulatory reporting systems. By implementing automated, multi-point validation checks during data migrations, the bank ensures the data feeding into its compliance reports is flawless, thereby mitigating the immense risk of regulatory fines and reputational damage.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To implement a robust validation strategy, consider these practical steps:
- Develop Reusable Validation Scripts: Create automated, reusable scripts to compare source and target data. Tools like QuerySurge or Informatica Data Validation can automate the testing of millions of records, checking for data type mismatches, value discrepancies, and referential integrity breaks.
- Involve Business Users in Acceptance Testing (UAT): Technical validation isn't enough. Engage accountants and financial analysts to perform User Acceptance Testing. They can spot issues that automated scripts might miss, such as a business rule that was technically migrated correctly but is logically flawed in its new context.
- Create Detailed Validation Reports: Generate comprehensive reports that summarize test results, including record counts, checksum comparisons, and a list of all discrepancies. These reports are invaluable for audit trails and provide concrete evidence that the migration was successful. For those handling raw data files, understanding how to manage formats is key; you can learn more about how to properly file CSV in Excel to support your manual validation efforts.
- Validate Business Logic Compliance: Go beyond technical accuracy. Test to ensure that complex business logic, such as interest calculations or risk-scoring algorithms, produces the exact same results in the new system as it did in the old one, using the same input data.
6. Effective Stakeholder Communication and Change Management
A data migration project is not just a technical exercise; it's a significant business transformation that impacts people and processes. Therefore, one of the most vital best practices for data migration is a robust strategy for stakeholder communication and change management. This practice involves systematically keeping everyone from the C-suite to end-users informed, engaged, and prepared for the changes the migration will bring. It’s about managing expectations, providing necessary training, and building buy-in across the organization.
Without effective change management, even a technically flawless migration can fail. Users who feel uninformed or unprepared may resist adopting the new system, leading to poor data entry, decreased productivity, and a failure to realize the project's intended ROI. A proactive communication plan turns potential resistance into active support, ensuring a smooth transition and rapid user adoption of the new financial systems.
Why It's a Foundational Step
Think of change management as the human-centric operating system for your migration project. Neglecting it is like giving someone a powerful new accounting tool without any instructions or explanation, then wondering why they aren't using it correctly. In a financial setting, the consequences are severe: accountants might revert to old spreadsheet-based workarounds, compromising data integrity, or a lack of clear communication could cause panic if a critical report is temporarily unavailable post-migration.
Toyota’s global ERP migration is a prime example of executing this well. They invested heavily in stakeholder engagement, creating a communication plan that addressed the specific concerns of finance teams in different regions. This ensured that everyone understood the benefits and was prepared for the new workflows, leading to a successful global rollout.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively integrate this practice into your migration project, consider these strategies:
- Create Stakeholder Maps: Begin by identifying all individuals and groups affected by the migration, from the CFO to accounting clerks. Map their level of influence and interest to tailor your communication strategy, ensuring the right message reaches the right audience.
- Tailor Communication Cadence: Not everyone needs a daily technical update. Executives may need a bi-weekly high-level summary, while the core project team needs daily stand-ups. Customize the frequency and detail of your communications for each stakeholder group.
- Provide Hands-On Training: Schedule comprehensive, role-based training sessions well before the system cutover. Allow users to practice in a sandbox environment to build confidence and proficiency with the new system and its impact on processes like cash flow management.
- Establish Clear Escalation Paths: Clearly define and communicate who to contact for different types of issues post-migration. This prevents confusion and ensures that problems are routed to the correct support team for rapid resolution, maintaining user trust.
- Celebrate Milestones: Acknowledge and celebrate key project milestones, such as the completion of data validation or a successful test run. This helps maintain positive momentum, boosts team morale, and keeps stakeholders engaged throughout the long migration lifecycle.
7. Automated Migration Tools and ETL Pipeline Implementation
Manually moving financial data is an antiquated, error-prone approach that has no place in a modern migration strategy. A far more robust and scalable approach involves leveraging specialized migration tools and building powerful pipelines to automate the entire process. This represents one of the most impactful best practices for data migration, as it systemizes data movement, transformation, and validation to reduce human error, enhance consistency, and create repeatable, auditable workflows.

The core of this practice is the implementation of pipelines that handle the heavy lifting. To streamline data transfer and ensure data quality, understanding key processes like Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes is essential. These automated systems extract data from the source, apply necessary transformations-like reformatting currency fields or reconciling account codes-and then load it into the target system with precision. This automation is crucial for handling the sheer volume and complexity of financial information.
Why It's a Foundational Step
Automating the migration process turns a high-risk, one-off project into a controlled, manageable, and repeatable operation. Without it, teams are left to manually script data transfers, which are difficult to test, impossible to scale, and incredibly fragile. For financial institutions, an automated pipeline provides a clear, documented audit trail for every record moved, which is invaluable for regulatory compliance and internal governance.
Consider Adobe's challenge of consolidating customer data from multiple acquired companies into a single platform. Using Informatica PowerCenter, they built robust ETL pipelines that automated the extraction, cleansing, and loading of billions of customer records. This not only ensured data integrity but also dramatically accelerated the integration timeline, allowing them to realize the value of their acquisitions faster.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively leverage automation in your migration, consider these strategies:
- Choose Compatible Tools: Select tools like AWS Glue, Talend, or Matillion that natively support both your source and target systems. Native connectors drastically simplify the setup and reduce the need for custom coding.
- Build Comprehensive Logging: From the very beginning, integrate detailed logging and monitoring into your pipelines. You need to be able to track every record, flag every error, and monitor performance in real-time.
- Create Reusable Components: Identify common transformation patterns (e.g., date formatting, address validation) and build them as reusable components. This modular approach speeds up development and ensures consistency across different data streams.
- Test with Representative Data: Before running the full migration, thoroughly test your tools and pipelines with a statistically significant sample of your production data to uncover edge cases and performance bottlenecks. These tools can also be part of a broader automation strategy; for more insight, you can explore information about bank statement extraction software.
8. Post-Migration Monitoring and Optimization
The go-live event is not the finish line; it’s the starting line for the new system's operational life. One of the most overlooked yet vital best practices for data migration is implementing a rigorous post-migration monitoring and optimization plan. This phase involves the continuous observation of the new environment to ensure it performs as expected, maintains data integrity, and meets user needs. It’s about proactively managing the health of your new system, from application response times to the accuracy of financial reports generated from the migrated data.
This ongoing vigilance allows you to catch and resolve issues that may not have been apparent during testing, such as performance bottlenecks that only appear under real-world transaction volumes. It transforms the migration from a one-time event into a continuous improvement cycle, ensuring the long-term value and stability of the investment. For example, a slow-running accounts payable report can be quickly identified and optimized before it impacts month-end closing procedures.
Why It's a Foundational Step
Think of this phase as the post-operative care for your data. A successful surgery (the migration) is pointless if the patient (the new system) isn't monitored for complications. Neglecting this step can lead to a gradual degradation of performance, erosion of user trust, and the re-emergence of data quality problems you worked so hard to fix. In a financial context, undetected performance issues could delay critical financial reporting, while subtle data drift could corrupt compliance audits over time.
A notable example is Slack's comprehensive monitoring strategy after its migration to AWS. By using a suite of monitoring tools, they were able to track performance metrics in real-time, identify unexpected system behaviors, and optimize resource allocation, ensuring a seamless experience for millions of users without service degradation.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively execute this practice, consider the following strategies:
- Establish Pre-Migration Baselines: Before the cutover, use tools like Datadog or New Relic to capture performance metrics (e.g., query speeds, CPU usage, report generation times) from your legacy system. These baselines are invaluable for making objective before-and-after comparisons.
- Set Up Automated Alerts: Configure automated alerts for critical performance thresholds and data quality anomalies. An alert should be triggered if, for instance, transaction processing time exceeds a certain limit or if a key financial data feed fails, enabling rapid response.
- Create a Stakeholder Reporting Cadence: Develop regular performance and data quality dashboards using tools like Grafana or Azure Monitor. Schedule weekly or bi-weekly reviews with key business users and IT stakeholders to discuss trends, issues, and optimization opportunities.
- Document and Socialize Lessons Learned: Conduct a post-mortem of the entire migration project. Document what went well and what could be improved, and share these insights across the organization. This creates a powerful knowledge base for future projects.
Best Practices Comparison for Data Migration
| Item | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comprehensive Data Assessment and Profiling | High (specialized tools and expertise needed) | High (time-intensive, expert involvement) | Improved data quality, better mapping accuracy | Early project phase, large/complex datasets | Reduces migration risks, enables accurate planning |
| Detailed Migration Planning and Strategy Development | Medium to High (structured frameworks, planning effort) | Medium to High (cross-team coordination) | Clear project direction, minimized business disruption | Complex migrations, stakeholder-heavy projects | Clear accountability, risk mitigation |
| Robust Data Backup and Recovery Procedures | Medium (setup and testing backup systems) | Medium to High (storage, testing resources) | Data protection, quick rollback capabilities | Migrations with critical data, high-risk environments | Safety net against data loss, supports compliance |
| Incremental and Phased Migration Approach | Medium to High (phase coordination complexity) | Medium (infrastructure for multiple phases) | Reduced risk, flexibility, minimized downtime | Large-scale migrations, high-risk data, phased rollout | Risk reduction, faster feedback, flexibility |
| Comprehensive Data Validation and Quality Testing | High (automation and validation scripting) | Medium to High (automation dev and testing) | Data integrity assurance, compliance support | Data-sensitive migrations requiring high accuracy | Ensures data quality, reduces post-migration issues |
| Effective Stakeholder Communication and Change Management | Medium (ongoing communication efforts) | Medium (dedicated communication resources) | Stakeholder alignment, reduced resistance | Organizational-wide migrations, user-impacting projects | Increases adoption, minimizes disruption |
| Automated Migration Tools and ETL Pipeline Implementation | Medium to High (tool setup and learning curve) | Medium to High (tool licenses, technical expertise) | Faster, consistent migration execution | Large data volume migrations, repeatable processes | Reduces manual effort, error reduction |
| Post-Migration Monitoring and Optimization | Medium (continuous effort post-migration) | Medium (monitoring tools and staff) | Sustained performance, continuous improvement | Post-migration stabilization, long-term system health | Proactive issue detection, supports ROI |
From Blueprint to Reality: Finalizing Your Data Migration Success
Successfully navigating a data migration is far more than a simple technical exercise; it's a strategic operation that hinges on meticulous planning, rigorous execution, and transparent communication. Throughout this guide, we've explored the eight pillars that form the foundation of a successful project. From the initial deep dive into data assessment and profiling to the final phase of post-migration monitoring and optimization, each step is an essential component of a cohesive and resilient strategy.
Adopting these best practices for data migration transforms what could be a high-risk, disruptive event into a powerful business enabler. You're not just moving records from one system to another; you are safeguarding the lifeblood of your financial operations, enhancing data integrity, and unlocking new potential for analytics and decision-making in the target environment. The journey from blueprint to reality is built on the principles we've discussed: foresight, validation, and a commitment to quality at every stage.
Recapping the Core Pillars of Migration Success
Let's distill the journey into its most critical takeaways. A successful migration isn't about excelling in one area but about achieving competence across the entire framework.
- Foundation First: The success of your entire project rests on the initial Comprehensive Data Assessment and Detailed Migration Planning. Without a clear understanding of what you have and a precise map of where you're going, you are navigating blind. This initial diligence prevents costly scope creep and unexpected roadblocks later on.
- Safety and Precision: Implementing Robust Data Backup procedures is your non-negotiable insurance policy. Pairing this with an Incremental and Phased Migration Approach allows you to manage risk effectively, minimize operational disruption, and build momentum through small, manageable victories.
- Trust but Verify: Data is only valuable if it's accurate. This is where Comprehensive Data Validation and Quality Testing becomes paramount. It’s the critical checkpoint that confirms your data has arrived intact, accurate, and ready for use. This isn't a step to be rushed; it's the ultimate confirmation of your project's integrity.
- The Human Element: Never underestimate the importance of Effective Stakeholder Communication and Change Management. A technically perfect migration can still fail if users don't understand, trust, or adopt the new system. Keeping everyone informed and involved fosters a smooth transition and ensures the project's long-term value is realized.
- Efficiency and Evolution: Leveraging Automated Migration Tools and establishing solid Post-Migration Monitoring are the final, crucial steps. Automation reduces manual error and accelerates the process, while ongoing optimization ensures your new system continues to deliver peak performance and business value long after the initial move is complete.
Your Path Forward: From Knowledge to Action
The ultimate goal of any data migration is not merely to relocate data but to enhance its accessibility, reliability, and strategic value. By internalizing and applying this comprehensive framework, you are equipped to lead your next financial data project with confidence and precision. You have the blueprint to de-risk the process, align technical execution with business objectives, and ensure the integrity of your most critical asset.
Think of these best practices not as a restrictive checklist but as a strategic compass. It guides you through complexity, helps you anticipate challenges, and empowers you to make informed decisions. By championing this structured approach, you position your organization to not only survive a data migration but to thrive because of it, ensuring your financial data continues to be a reliable foundation for growth and innovation.
Before you begin your next major migration, you often need to tackle smaller, more immediate data challenges. If your process involves converting unstructured financial documents like bank statements into clean, usable data, explore how Bank Statement Convert PDF can streamline this critical first step. Our specialized tool helps you quickly and accurately extract data, ensuring the information you migrate is clean and structured from the start. Visit us at Bank Statement Convert PDF to see how we can simplify your data preparation.


